|
设计描述:
文档包括:
设计说明书1份,共155页,约75000字左右
CAD版本图纸,共5张
毕业设计任务书
毕业设计题目:涡北煤矿1.5 Mt/a新井设计
毕业设计专题题目:浅析深井沿空留巷支护理论与技术
毕业设计主要内容和要求:
本设计包括三个部分:一般部分、专题部分和翻译部分。
一般部分
题目为涡北煤矿1.50 Mt/a新井设计。井田走向长度约6 km,倾向长度约3.2 km,面积约19 km2。主采煤层为8号煤层,平均倾角为18°,平均厚度为9.0 m。井田工业储量为191.87 Mt,可采储量为111.03 Mt,矿井服务年限为56.9 a。
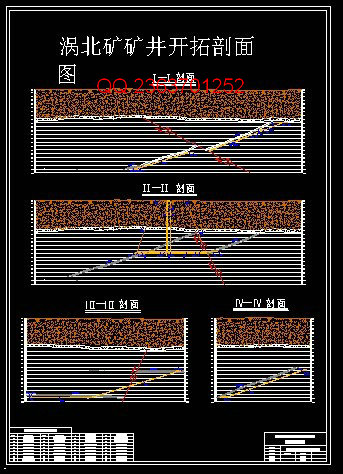
根据井田地质条件,提出四个技术上可行的开拓方案。通过技术经济比较,最终确定方案三为最优方案。一水平标高-650 m,二水平标高-1000 m。
设计首采区采用采区准备方式,工作面长度200 m,采用综采放顶煤采煤法,矿井年工作日为330 d,工作制度为“三八制”。
大巷采用胶带输送机运煤,辅助运输采用矿车运输。矿井通风方式为中央并列式。
专题部分
题目:浅析深井沿空留巷支护理论与技术。深井沿空留巷是提高采出率、煤层群卸压开采,进而实施煤与瓦斯共采的关键技术。要经历两次工作面采动影响,加之深部巷道围岩变形具有高地压、大变形和长期蠕变的特点,巷道维护较浅部沿空留巷更加困难。本文以淮南顾桥煤矿深井沿空留巷为工程背景,运用FLAC3D数值模拟和现场实测相结合的手段对工程实践中经常遇到的厚直接顶、薄直接顶和无直接顶三种沿空留巷类型进行研究,提出相应的支护方案。
翻译部分
题目:Numerical simulation of rock burst in circular tunnels under unloading conditions。
摘 要
本设计包括三个部分:一般部分、专题部分和翻译部分。
一般部分为涡北煤矿1.50 Mt/a新井设计。涡北煤矿位于安徽省亳州市境内,东有京九铁路,西有濉阜铁路,交通便利。井田走向长度约6 km,倾向长度约3.2 km,面积约19 km2。主采煤层为8号煤层,平均倾角为18°,平均厚度为9.0 m。井田工业储量为191.87 Mt,可采储量为111.03 Mt,矿井服务年限为56.9 a。矿井正常涌水量为250 m3/h,最大涌水量为280 m3/h。矿井绝对瓦斯涌出量为21.33 m3/min,属于低瓦斯矿井。
根据井田地质条件,提出四个技术上可行的开拓方案。方案一:立井两水平开拓上下山开采,暗斜井延深;方案二:立井两水平开拓上下山开采,立井直接延深;方案三:立井两水平开拓上山开采,暗斜井延深;方案四:立井两水平开拓上山开采,新混合井延深。通过技术经济比较,最终确定方案三为最优方案。一水平标高-650 m,二水平标高-1000 m。
设计首采区采用采区准备方式,工作面长度200 m,采用综采放顶煤采煤法,矿井年工作日为330 d,工作制度为“三八制”。
大巷采用胶带输送机运煤,辅助运输采用矿车运输。矿井通风方式为中央并列式。
专题部分题目:浅析深井沿空留巷支护理论与技术。深井沿空留巷是提高采出率、煤层群卸压开采,进而实施煤与瓦斯共采的关键技术。要经历两次工作面采动影响,加之深部巷道围岩变形具有高地压、大变形和长期蠕变的特点,巷道维护较浅部沿空留巷更加困难。本文以淮南顾桥煤矿深井沿空留巷为工程背景,运用FLAC3D数值模拟和现场实测相结合的手段对工程实践中经常遇到的厚直接顶、薄直接顶和无直接顶三种沿空留巷类型进行研究,提出相应的支护方案。
翻译部分题目:Numerical simulation of rock burst in circular tunnels under unloading conditions。圆形隧道在卸压过程中发生岩爆的数值模拟。
关键词: 立井; 暗斜井; 采区布置; 放顶煤采煤法; 中央并列式; 沿空留巷
ABSTRACT
This design can be divided into three sections: general design, monographic study and translation of an academic paper.
The general design is about a 1.50 Mt/a new underground mine design of Wobei coal mine.Wobei coal mine lies in Hozhou City, Anhui province.As Jingjiu railway runs in the west of the mine field and Suifu railway runs in the east of the mine field, the traffic is convenient.It’s about 6 km on the strike and 3.2 km on the dip, with the 19 km2 total horizontal area.The minable coal seam is 8 with an average thickness of 9.0 m and an average dip of 18°.The proved reserves of this coal mine are 191.87 Mt and the minable reserves are 111.03 Mt, with a mine life of 56.9 a. The normal mine inflow is 250 m3/h and the maximum mine inflow is 280 m3/h. The mine gas emission rate is 21.33 m3/min, the mine belongs to low gas mine.
Based on the geological conditions of the mine, I bring forward four available projects in technology.The first is vertical shaft development with two mining levels and the first level at -650m and the second level at -850m and extension of blind inclined shaft; the second is vertical shaft development with two mining levels and the first level at -650m and the second level at -850m and extension of vertical shaft; the third is vertical shaft development with two mining levels and the first level at -650m and the second level at -1000m and extension of blind inclined shaft; the last is vertical shaft development with two mining levels and the first level at -650m and the second level at -1000m and extension of new vertical shaft. The third project is the best comparing with other three projects in technology and economy.The first level is at -650 m.The second level is at -1000 m.
Designed first mining district makes use of the method of the mining district preparation.The length of working face is 200 m, which uses fully-mechanized coal caving mining method. The working system is “three-eight” which produces 330 d/a.
Main roadway makes use of belt conveyor to transport coal resource, and mine car to be assistant transport. The type of mine ventilation system is center ventilation.
The monographic study is a brief analysis of law and tecenolgy of rodway supporting of gob-side entry rataining.Gob-side entry rataining is the key technology of unlonding stress and coal and gas mining at the same time. Because of twice mining influence, high press and large deformation and long-term creep of the deep roadway, it’s more difficult to roadway maintenance.The paper is based on the deep gob-side entry retaining of Guqiao coalmine in Huaibei mining area. And it researches on the laws of stress evolution and failure mechanism of roadway with thick roof and thin roof and no roof by using numerical simulation and applying field test, and proposes corresponding support scheme.
The translated academic paper is Numerical simulation of rock burst in circular tunnels under unloading conditions.
Keywords: Vertical shaft; Blind inclined shaft; Mining district preparation; Coal caving mining ; Center ventilation; Gob-side entry rataining
目 录
一 般 部 分
1 矿区概述及井田地质特征 3
1.1矿区概述 3
1.1.1地理位置与交通 3
1.1.2地形地貌 3
1.1.3河流及水体 3
1.1.4气候 3
1.1.5自然地震 3
1.1.6矿区内工农业生产、建筑材料等概况 3
1.1.7区域电源 3
1.2井田地质特征 3
1.2.1地层 3
1.2.2井田地质构造 3
1.2.3水文地质条件 3
1.3煤层特征 3
1.3.1煤层 3
1.3.2煤层顶底板 3
1.3.3煤质及工业用途 3
1.3.4瓦斯 3
1.3.5煤尘 3
1.3.6煤的自燃 3
1.3.7地温 3
2 井田境界和储量 3
2.1井田境界 3
2.1.1井田范围 3
2.1.2开采界限 3
2.1.3井田尺寸 3
2.2矿井工业储量 3
2.2.1地质资源储量 3
2.2.2工业资源/储量 3
2.3矿井可采储量 3
2.3.1安全煤柱留设原则 3
2.3.2矿井永久保护煤柱损失量 3
2.3.3矿井可采储量 3
3 矿井工作制度、设计生产能力及服务年限 3
3.1矿井工作制度 3
3.2矿井设计生产能力及服务年限 3
3.2.1确定依据 3
3.2.2矿井设计生产能力 3
3.2.3服务年限 3
3.2.4井型校核 3
4 井田开拓 3
4.1井田开拓的基本问题 3
4.1.1确定井筒形式、数目、位置及坐标 3
4.1.2工业场地的位置 3
4.1.3阶段划分及开采水平的确定 3
4.1.4主要开拓巷道 3
4.1.5矿井开拓延深 3
4.1.6方案比较 3
4.2矿井基本巷道 3
4.2.1井筒 3
4.2.2井底车场及硐室 3
4.2.3主要开拓巷道 3
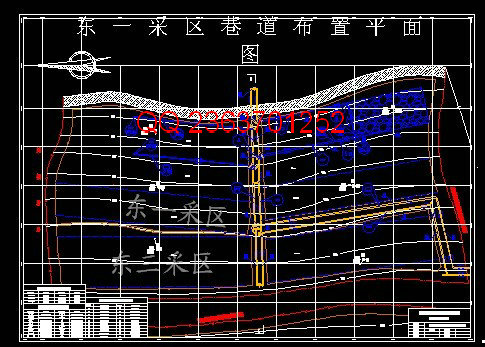
5 准备方式—采区巷道布置 3
5.1煤层地质特征 3
5.1.1采区位置 3
5.1.2采区煤层特征 3
5.1.3煤层顶底板岩石构造情况 3
5.1.4水文地质 3
5.1.5主要地质构造 3
5.1.6地表情况 3
5.2采区巷道布置及生产系统 3
5.2.1采区范围及区段划分 3
5.2.2煤柱尺寸的确定 3
5.2.3采煤方法及首采工作面工作面长度的确定 3
5.2.4确定采区各种巷道的尺寸、支护方式 3
5.2.5采区巷道的联络方式 3
5.2.6采区接替顺序 3
5.2.7采区生产系统 3
5.2.8采区内巷道掘进方法 3
5.2.9采区生产能力及采出率 3
5.3采区车场选型设计 3
6 采煤方法 3
6.1采煤工艺方式 3
6.1.1采区煤层特征及地质条件 3
6.1.2确定采煤工艺方式 3
6.1.3回采工作面参数 3
6.1.4回采工艺及设备 3
6.1.5回采工作面支护方式 3
6.1.6端头支护及超前支护方式 3
6.1.7各工艺过程注意事项 3
6.1.8回采工作面正规循环作业 3
6.2回采巷道布置 3
6.2.1回采巷道布置方式 3
6.2.2回采巷道参数 3
7 井下运输 3
7.1概述 3
7.1.1井下运输设计的原始条件和数据 3
7.1.2运输距离和货载量 3
7.1.3矿井运输系统 3
7.2采区运输设备选择 3
7.2.1设备选型原则 3
7.2.2采区运输设备的选型 3
7.3大巷运输设备选择 3
7.3.1运输大巷设备选择 3
7.3.2辅助运输大巷设备选择 3
8 矿井提升 3
8.1概述 3
8.2主副井提升 3
8.2.1主井提升 3
8.2.2副井提升 3
9 矿井通风及安全 3
9.1矿井地质、开拓、开采概况 3
9.1.1矿井地质概况 3
9.1.2开拓方式 3
9.1.3开采方法 3
9.1.4变电所、充电硐室、火药库 3
9.1.5工作制、人数 3
9.2矿井通风系统的确定 3
9.2.1矿井通风系统的基本要求 3
9.2.2矿井通风方式的选择 3
9.2.3矿井通风方法的选择 3
9.2.4采区通风系统的要求 3
9.2.5工作面通风方式的确定 3
9.1.6回采工作面进回风巷道的布置 3
9.3矿井风量计算 3
9.3.1矿井风量计算方法概述 3
9.3.2回采工作面风量计算 3
9.3.3掘进工作面风量计算 3
9.3.4硐室需要风量的计算 3
9.3.5其他巷道所需风量 3
9.3.6矿井总风量计算 3
9.3.7风量分配 3
9.4矿井通风阻力 3
9.4.1确定矿井通风容易时期和困难时期 3
9.4.2矿井通风容易时期和困难时期的最大阻力路线 3
9.4.3矿井通风阻力计算 3
9.4.4矿井通风总阻力 3
9.4.5矿井总风阻及总等积孔 3
9.5矿井通风设备选型 3
9.5.1通风机选择的基本原则 3
9.5.2通风机风压的确定 3
9.5.3电动机选型 3
9.5.4矿井主要通风设备的要求 3
9.5.5对反风装置及风硐的要求 3
9.6特殊灾害的预防措施 3
9.6.1预防瓦斯和煤尘爆炸的措施 3
9.6.2预防井下火灾的措施 3
9.6.3防水措施 3
10 设计矿井基本技术经济指标 3
参考文献 3
专 题 部 分
浅析深井沿空留巷支护理论与技术 3
1绪论 3
1.1 问题的提出与研究意义 3
1.2研究现状 3
1.3研究内容及研究方法 3
2沿空留巷围岩结构 3
3沿空留巷围岩应力分布 3
4留巷侧采空区顶板的运动规律 3
5巷旁支护的作用及形式 3
6巷内支护形式的选择 3
7沿空留巷矿压显现规律的数字模拟和现场实测 3
7.1沿空留巷矿压显现规律的数值模拟 3
7.2沿空留巷矿压显现规律的现场实测 3
8 结论 3
翻 译 部 分
英文原文 3
中文译文 3
致 谢 3
|