|
文档包括:
word说明书一份,共115页,约53000字
CAD版本图纸,共4张
摘 要
本设计包括三个部分:一般部分、专题部分和翻译部分。
一般部分为永煤集团车集煤矿240万t/a新井设计。全篇共分为十个部分:矿井概况及井田地质特征、井田境界及储量、矿井工作制度、设计生产能力、井田开拓、矿井基本巷道、采煤方法、采区巷道布置、井下运输、矿井提升、矿井通风与安全和矿井主要经济技术指标。
车集矿位于河南省永夏矿区东南部。井田南北走向平均长10.76km,东西平均宽4.1km,面积约44.01km2。 井田内可采煤层为二2煤,其赋存稳定,厚度平均3.5m,倾角平均10°,为缓倾斜煤层。井田内工业储量为25026.78万t,可采储量为18210.9万t。矿井平均涌水量为727 m3/h,相对瓦斯涌出量为2.5m3/t,属低瓦斯矿井;煤尘无爆炸性危险,无自燃发火倾向;地温29~30℃。
车集煤矿年设计生产能力为240万t/a,服务年限为58.37年。采用立井开拓,暗斜井延深的开拓方式。工作制度为“四六”制。第一水平标高为-600m,第二水平标高为-850m。矿井采用倾斜长壁综合机械化采煤法,一次采全高。
矿井布置一个综采工作面,面长160m。煤炭通过胶带输送机运输。矿井通风方式为两翼对角式。
专题部分:专题题目为“FLAC在井下开挖工程中的应用与分析”。
翻译部分:将FLAC 4.0版的英文说明书的Introduction的一部分翻译成中文。英文题目是“Primer of FLAC”。
ABSTRACT
This design contains three parts: the general,the special subject and the translation.
The general part is a new design of Juji Mine in Yongcheng coal & eletricity combine. The whole article is divided into ten parts: the outline of the mine, the mine field geology, the boundary and reserves, the designed productive capacity, the service life and working area, the coal transportation, the mine lifting, the ventilation and safety, and the main economical and technological index of the mine.
The Juji Mine field lies in the southeast part of the Yongxia mineral District in Henan province. The boundary of the mine field runs 10.76km from north to south and 4.1km from west to east on average. The total plane area of the mine is about 44.01km2. There is only one exploring layer--number two. Its average thickness of the seam is 3.5m and it’s stable and flatly inclined. Its dip angle is 10 degree on average. The industry reserves of the mine field are 250.27 million tons and the useable reserves are 182.11 million tons. The average inflow rate in Juji mine is 727 m3/h. It is a lower gassy mine. The coal dust doesn’t have explosion hazard as well as the self-combustion tendency.
The productive capacity of Juji Mine is 2.4 million tons per year,and the service life is 58.37 years. The work system is 4-shift with a 6-hour workday. There’re two working levels in the mine. The first development level is located at the -600m, and the second is at the level of -850m. The comprehensive mechanized longwall caving method along the dip is used in Juji Mine.
There is only one working face in the mine. It is comprehensive mechanized coal face. The length of the face is 160m, and the designed productive capacity of the face is 2.4 million tons per year. Coal is transported by belt conveyer and the diagonal ventilation system is used in Juji.
The title of special subject is “the application and analysis of FLAC used in underground engineering”.
The translation part is to translate a part of the Introduction of English manual of FLAC 4.0 versions into the Chinese. And it titled "The Primer of FLAC".
目 录
一般部分
1 矿区概述及井田地质特征 1
1.1 矿区概述 1
1.1.1 交通位置 1
1.1.2 河流 1
1.1.3 矿区气候条件 1
1.1.4 地震 2
1.1.5 水源电源 2
1.2 井田地质特征 2
1.2.1 井田地形及煤系地层概述 2
1.2.2 井田地质构造 3
1.2.3 井田水文地质 4
1.3 井田煤层特征 5
1.3.1 煤层埋藏条件及围岩性质 5
1.3.2 煤层特征 6
2 井田境界与储量 8
2.1 井田境界 8
2.1.1 井田境界划分的原则 8
2.1.2 井田境界 8
2.2 矿井工业储量 8
2.2.1 井田勘探类型 8
2.2.2 矿井工业储量的计算及储量等级的圈定 8
2.3 矿井可采储量 9
2.3.1 计算可采储量时,必须要考虑以下储量损失 9
2.3.2 各种煤柱损失计算 9
2.3.3 井田的可采储量 12
3 矿井工作制度、设计生产能力及服务年限 14
3.1 矿井工作制度 14
3.2 矿井设计生产能力服务年限 14
3.2.1 矿井设计生产能力 14
3.2.2 井型校核 14
4 井田开拓 16
4.1 井田开拓的基本问题 16
4.1.1 影响井田开拓的主要因素 16
4.1.2 井筒形式、数目的确定 16
4.1.3 工业广场的位置、形状和面积的确定 19
4.1.4 开采水平的确定 19
4.1.5 井底车场和运输大巷的布置 19
4.1.6 矿井开拓延伸及深部开拓方案 20
4.1.7 开采顺序 20
4.1.8 方案比较 20
4.2 矿井基本巷道 27
4.2.1 井筒 27
4.2.2 井底车场 31
4.2.3 主要开拓巷道 32
4.2.4 巷道支护 33
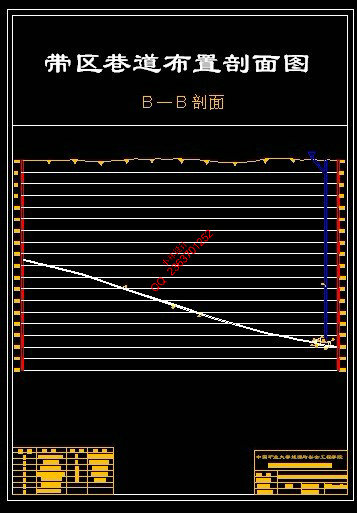
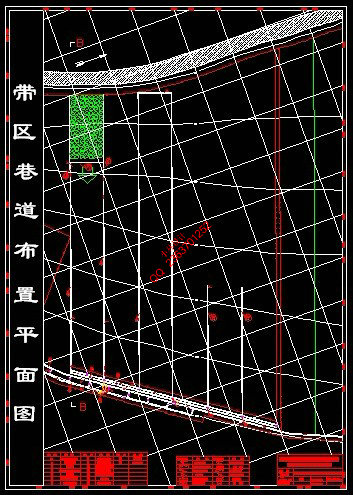
5 准备方式——带区巷道布置 35
5.1 煤层的地质特征 35
5.1.1 首采带区煤层特征 35
5.1.2 地质构造 35
5.1.3 顶底板特征 35
5.1.4 水文地质 35
5.1.5 地表情况 35
5.2 首采带区巷道布置及生产系统 36
5.2.1 带区位置及范围 36
5.2.2 采煤方法及工作面长度的确定 36
5.2.3 确定带区各种巷道的尺寸、支护方式及通风方式 36
5.2.4 煤柱尺寸的确定 36
5.2.5 带区巷道的联络方式 37
5.2.5 带区接替顺序 37
5.2.6 带区生产系统 37
5.2.7 带区内各种巷道的掘进方法 38
5.2.8 带区生产能力 38
5.3 带区车场选型设计 39
5.3.1 确定带区车场形式 39
5.3.2 带区主要硐室布置 39
6 采煤方法 41
6.1 采煤工艺方式 41
6.1.1 采煤方法的选择 41
6.1.2 回采工作面长度的确定 41
6.1.3 工作面的推进方向和推进度 41
6.1.4 综采工作面的设备选型及配套 43
6.1.5 采煤机的工作方式 48
6.1.6 工作面端头支护 49
6.1.7 循环图表、劳动组织、主要技术经济指标 50
6.1.8 综合机械化采煤过程中应注意事项 54
6.2 回采巷道布置 55
6.2.1 带区巷道布置 55
6.2.2 保护煤柱尺寸的确定 56
6.2.3 巷道掘进方法 58
6.2.4 巷道支护方式 58
6.2.5 通风验算 59
7 井下运输 60
7.1 概述 60
7.1.1 井下运输设计的原始条件和数据 60
7.1.2 矿井运输系统 60
7.2 带区运输设备的选择 61
7.2.1 矿井运输设备选型应主要遵循以下原则: 61
7.2.2 工作面运煤设备的选型 62
7.2.3 带区辅助运输设备的选型与设计 62
7.2.4 大巷运输设备选择 62
8 矿井提升 65
8.1 概述 65
8.2 主副井提升 65
8.2.1 已知数据 65
8.2.2 主井提升机械设备的选型设计 65
8.2.3 副井提升 66
9 矿井通风 67
9.1 矿井通风系统的选择 67
9.1.1 矿井概况 67
9.1.2 矿井通风系统的基本要求 67
9.1.3 矿井通风方式的确定 67
9.1.4 矿井主扇工作方法的选择 70
9.1.5 确定带区内通风系统 71
9.1.6 确定回采工作面通风 72
9.1.7 确定矿井通风容易时期和困难时期及其用风地点 72
9.2 矿井风量计算及风量分配 74
9.2.1 选择通风系统的原则和方法 74
9.2.2 配风依据 75
9.2.3 风量计算 75
9.3 计算矿井的通风阻力 80
9.3.1 计算原则 80
9.3.2 矿井最大阻力路线 81
9.3.3 各段通风阻力 81
9.3.4 全矿通风总阻力 82
9.3.5 两个时期的矿井总风阻和总等积孔 83
9.4 选择矿井通风设备 83
9.4.1 选择通风机的基本原则 83
9.4.2 通风机的选型 84
9.4.3 电动机的选择 86
9.4.4 对矿井主要通风设备的要求 88
9.4.5 对反风、风峒的要求 88
9.5 矿井灾害的防治措施 89
9.5.1 瓦斯管理措施 89
9.5.2 煤尘的防治 89
9.5.3 防火 90
9.5.4 防水 90
10 设计矿井基本技术经济指标 91
专题部分
FLAC在井下开挖工程中的应用和分析 93
1 数值模拟软件——FLAC简介 94
1.1 FLAC软件设计的基本算法 94
1.2 FLAC软件优、缺点 94
1.3 FLAC主要用于解决以下典型问题 95
1.4 FLAC基本术语 96
1.5 FLAC的工作流程 96
2 FLAC应用实例 97
2.1 山东里能集团新河煤矿煤巷锚网支护基本参数优化设计 97
2.1.1 现场基本参数和数值计算模型 97
2.1.2 模型建立 99
2.1.3 计算结果分析 99
2.1.4 小结 104
2.2 河南永煤集团某基建矿井底车场交叉点巷道数值模拟 104
2.2.1 现场基本参数和数值计算模型 105
3 FLAC数值模拟结论 110
翻译部分
Primer of FLAC 112
1 Overview 112
2 Comparison with Other Methods 115
FLAC入门知识 117
1 概述 117
2 和其他的方法比较 119
附图
附图 车集矿井综合柱状图 120
|