|
设计简介 |
设计描述:
文档包括:
word说明书一份,共49页,约15000字
CAD版本图纸,共24张
摘 要
气动机械手是以气压为驱动力的机械手。机械手并不是在简单意义上代替人工的劳动,而是综合了人的特长和机器特长的一种拟人的电子机械装置,既有人对环境状态的快速反应和分析判断能力,又有机器可长时间持续工作、精确度高、抗恶劣环境的能力,它主要是用以按固定程序抓取、搬运物件或操作工具的自动操作装置。所以气动机械手能够降低劳动强度,提高生产效率。但它的缺点也很明显,因为气体具有很大的可压缩性, 要做到气动机械手精确定位难度很大, 尤其是难以实现任意位置的多点定位;而且可压缩性也带来不能承受过重的负载的限制。传统气动系统只能靠机械定位置的调定位置而实现可靠定位, 并且其运动速度只能靠单向节流阀单一调定, 经常无法满足许多设备的自动控制要求。
本课题经过深刻的研究发现,目前生产线上的气动翻转机械手一个运动进程只能实现一次抓取和翻转功能的,感觉这种机械手效率太低。所以本次设计针对这个缺点,设计出了一种气动翻转机械手,它在一个运动进程能实现两次抓取和翻转,提高了工作效率,加快生产效率。全文由五章构成:
关键词:气动装置;机械手;翻转装置;夹瓶器
Abstract
Pneumatic manipulator is a robot which is based on Pressure-driven. The robot is the combination of expertise and expertise of an anthropomorphic machine electro-mechanical device, not simply instead of manual labor. It owns both the rapid response to the environment state and the ability of a long continuous operation, high accuracy, and the resistance to harsh environments. It is mainly used to crawl at a fixed program, and carry objects and operate tools automatically. So Pneumatic Manipulator can reduce labor intensity, improve production efficiency. However, its disadvantages are obvious. Pneumatic Manipulator getting the precise positioning is very difficult, especially achieving multi-point positioning to anywhere because of the great compressibility of gas. Also, the compressibility limits a load to be too heavy. Traditional pneumatic system only relies on the set position of the mechanical giving location and reliable positioning and velocity which relies on a single one-way throttle. So it is often unable to meet many requirements of the automatic control equipment.
After a deep study, we found that the pneumatic flip robot on the current production line can only be achieved crawling and flip function once in a movement process whose efficiency is too low. So we design a pneumatic flip robot which can achieve the two crawling and flipping in a motion process. There is no doubt that the pneumatic flip robot can improve work efficiency and speed up the production efficiency.
Key words: pneumatic devices; robot; turning device; clip bottle;
目 录
摘 要
Abstract
第1章 绪论 1
1.1 引言 1
1.2气动机械手的发展 1
1.2.1国外气动机械手状况 1
1.2.2国内气动机械手情况 3
1.3发展趋势 3
1.3.1重复高精度 3
1.3.2模块化 3
1.3.3无给油化 4
1.3.4 机电气一体化 4
1.4 机械手夹持部件结构示意图 4
1.4.1 外夹持型机械手 4
1.4.2 内夹持型机械手 5
1.5国内外气动机械手设计举例 5
1.5.1与模具切割相结合 5
1.5.2 机械手虚拟样机 6
1.5.3 高精度机械手 6
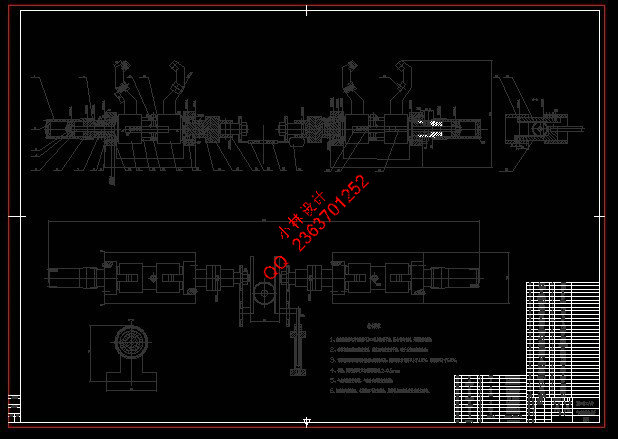
第2章 气动翻转机械手总体设计 8
2.1 抓取系统的初步设计 8
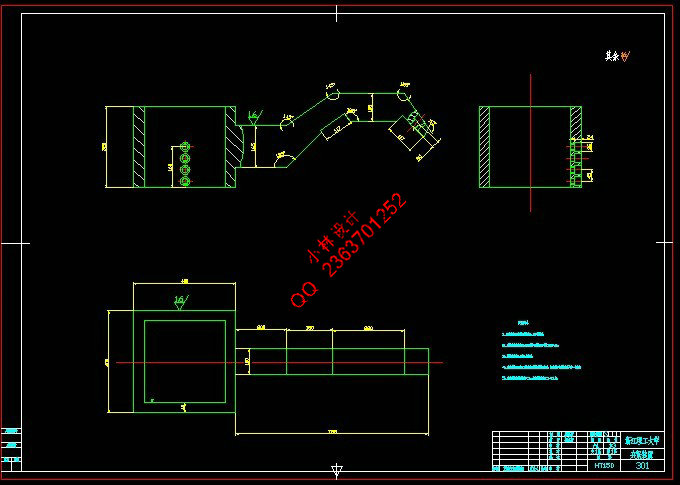
2.2 翻转系统的初步设计 8
2.2.1 锥齿轮电机翻转 8
2.2.2 链轮链条气缸翻转 9
2.2.3 翻转方案选择 9
2.3气动翻转机械手的三维建模、装配思路 10
2.3.1各部分零件设计 10
2.3.2 气动翻转机械手的运动学仿真 10
2.3.3 研究思路方案、可行性分析及预期成果 11
第3章 气动翻转机械手重要零部件设计校核及其装配 12
3.1气缸的设计和校核 12
3.1.1 夹紧系统气缸设计和校核 12
3.1.2 翻转系统气缸设计和校核 14
3.2齿轮设计和校核 15
3.2.1齿轮参数的选择 15
3.2.2齿轮几何尺寸确定 15
3.2.3齿根弯曲疲劳强度计算 16
3.3齿条的设计和校核 18
3.3.1齿条的设计 18
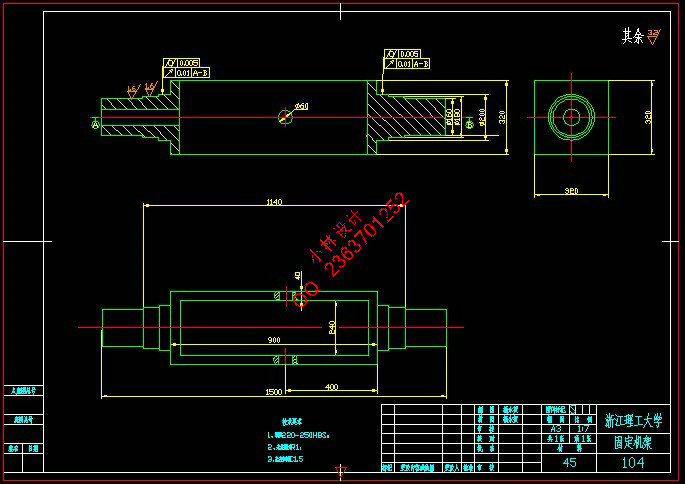
3.4 固定机架上的轴设计和校核 20
3.4.1求输入轴上的功率、转速和转矩 20
3.4.2求作用在齿轮上的力 20
3.4.3 初步确定轴的最小直径 21
3.4.4轴的结构设计 21
3.4.5精确校核轴的疲劳强度 23
3.5圆锥滚子轴承的设计和校核 25
3.6键连接设计和校核 26
3.6.1输入轴键计算 26
3.6.2中间轴键计算 26
3.6.3输出轴键计算 27
3.7联轴器的设计和校核 27
第4章 三维建模和运动仿真 29
4.1 整体装配图 29
4.2夹紧系统装配图 29
4.3气缸推动和翻转系统装配图 30
4.4 气缸推动夹紧装置系统装配图 30
第5章 总结与展望 32
5.1总结 32
5.2展望 32
参考文献 33
致 谢 35
|