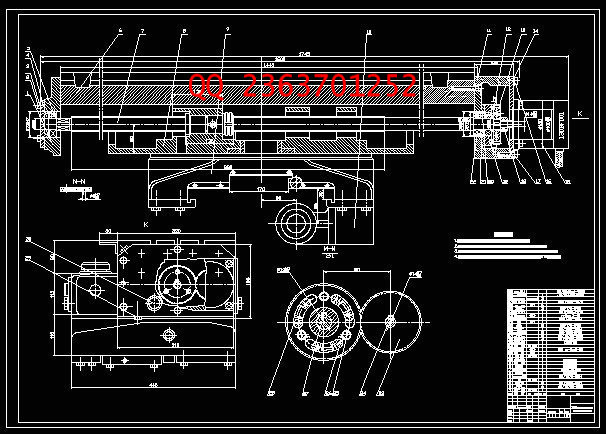
|
设计描述:
文档包括:
设计word版本说明书一份,共33页,约9500字、
CAD版本图纸,共6张
目 录
0摘要----------------------------------------------------------------------3
第一章 概述 ------------------------------------------------------------------------5
1.1 课题概述与设计目的------------------------------------------------5
1.2 设计课题--------------------------------------------------------------9
第二章 设计说明-----------------------------------------------------------------10
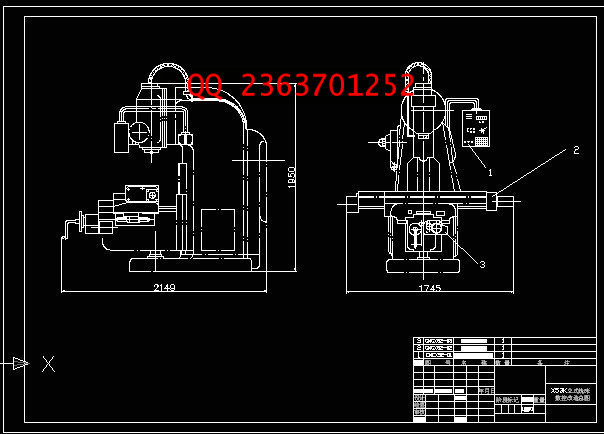
2.1 总体方案的确定及框图-------------------------------------------10
2.2 机械部分设计计算 ------------------------------------------------11
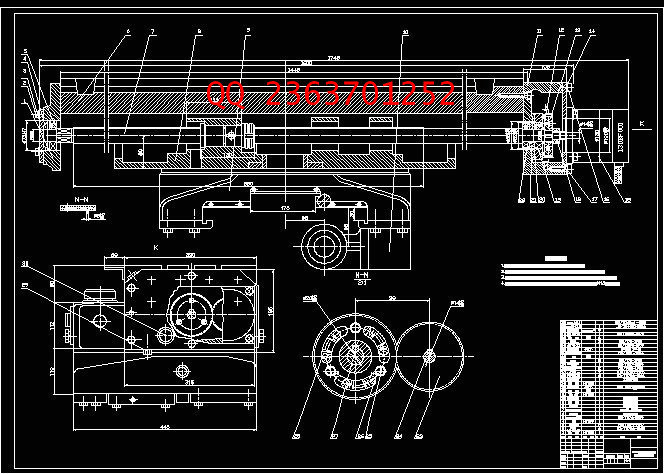
2.3 进给伺服系统结构设计-------------------------------------------17
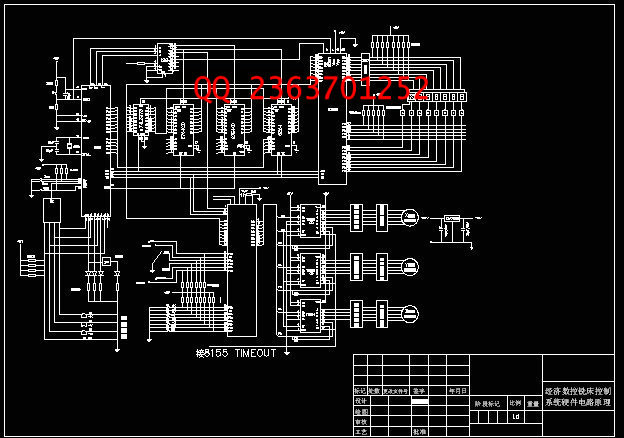
2.4硬件部分电路的设计----------------------------------------------19
2.5 凸轮加工程序------------------------------------------------------24
第三章 毕业设计体会----------------------------------------------------------26
3.1毕业设计体会-------------------------------------------------------26
参考资料----------------------------------------------------------------------------28
摘要
在过去二十年间,工业上已应用机器人来完成使操作人员感到厌烦和紧张的那些单调而又不安全的操作。由于机器人完成某些操作要比人更快,更精确,故在各种制造工业中的应用愈来愈广泛。对多数大型制造业(如汽车工业)来说,为保持其具有竞争性,必须大规模采用机器人。目前,机器人已广泛应用在点焊和缝焊、装配部件、移动重物、喷漆、重复加工等操作中,。
为使机器人能完成上述这些操作,必须使用小型计算机对机器人进行编程。小型计算机不仅要对机器人发出完成所要求工步的指令,而且还要能记忆程序。由操作人员(或程序员)将信息反馈给小型计算机个CRT或视频显示所组成的控制装置。操作人员可以随时改编原有程序,即:删除或插入任何所要求的工步。
关键字:加工精度,设计方案,分配,参数
ABSTRACT
Over the past two decades the robot has been introduced into industry to perform many monotonous and often unsafe operations which in the past had caused both boredom and stress among employees. Because robots can perform certain basic tasks more quickly and accurately than humans they are being increasingly used in various manufacturing industries. In order for most of the larger manufacturing industries, such as the automotive industry, to remain competitive it has been necessary for them to introduce robots on quite a large scale. Robots are now used extensively for such operations as spot and seam welding, assembling components, moving heavy parts, spray painting, and repetitive machining operations.
In order for a robot to perform these tasks it must be programmed by a minicomputer, which will not only direct the robot to perform the required steps but will also “remember” the sequence. Information is fed by the operator (or programmer) into a control unit consisting of the minicomputer and a cathode ray tube (CRT) or video display. The operator can, at any time, edit a previous program by deleting or adding any desired steps.
KeyWords: Accuracy of Process,Project Design,Allotment,Parameter
|