|
设计描述:
文档包括:
WORD版设计说明书1份,共85页,约29000字
任务书一份
外文翻译一份
CAD版本图纸,共10张
第一章 原始资料分析
摘 要
本设计是黑龙江G市污水处理厂的初步设计,主要任务是完成污水及污泥处理方法选择、工艺设计计算、污水厂平面图、高程图及单项处理构筑物施工图设计。
该城市排放的污水中BOD5、CODcr及SS严重超标,依据污水的水质、水量以及受纳水体的环境容量等相关资料,必须对其进行二级处理方可去除水中过量的有机污染物,达到排放标准进而保护环境,所以本设计采用SBR序列间歇式活性污泥法。
SBR是序列间歇式活性污泥法的简称,与传统污水处理工艺不同,SBR技术采用时间分割的操作方式替代空间分割的操作方式,非稳定生化反应替代稳态生化反应,静置理想沉淀替代传统的动态沉淀。它的主要特征是在运行上的有序和间歇操作,SBR技术的核心是SBR反应池,该池集均化、初沉、生物降解、二沉池等功能于一池,无污泥回流系统。经过这个废水处理工艺的废水可达到设计要求,可以直接排放。处理后的污泥经机械脱水后用作肥料。
通过此设计,污水处理厂建成后,本市的水污染问题能得到较好的解决,产生良好的环境效益,同时也会收到很好的经济效益和社会效益。
关键词: SBR工艺;污水处理厂;城市污水;活性污泥
Abstract
This is the preliminary design of the sewage treatment plant of city G in Heilongjiang Province. The main task of this project is to complete the scheme selection of sewage and sludge treatment design computation and design the sewage plant horizontal plan elevation map and construction drawing of the monomer structure.
The contents of BOD5、CODcr and SS of the discharged sewage have surpassed the national standard in this city. It must be used secondary treatment to remove excess organic pollutants in sewage in order to meet discharge standards and protect environment,which is based on the quality and quantity of sewage the environmental capacity of the receiving water bodies and other relevant information. Therefore,sequencing batch reactor activated sludge process was used in this design.
SBR is the abbreviation of the sequencing batch reactor activated sludge process. Different from traditional sewage treatment process, SBR technology uses to substitute time division operation mode for space division, non-stable biochemical reactions for stable state, ideal precipitation for the traditional dynamic precipitation. The main feature is the sequencing and batch operation. The core of the SBR technology is SBR tank, which sets all of the functions of homogenization, primary sedimentation, biodegradation and secondary sedimentation in a tank, and no sludge return system. The outlet water of the plant meets the design requirements, which is allowed direct discharge into rivers. The treated sludge is used for fertilizer after mechanical dewatering.
Water pollution problems of this city can be solved when the sewage treatment plant is completed. It has very good environmental benefits economic and social benefits.
Key words: SBR process;sewage treatment plant;urban sewage;activated sludge
目 录
第1章 绪论 1
1.1 概述 1
1.1.1 环境概述 1
1.1.2 本设计的目的和依据 1
1.1.3 设计内容 1
1.2 设计原始资料 2
1.2.1 气象资料 2
1.2.2 地质资料 2
1.2.3 水质与水量资料 2
1.2.4 纳污水体的水文和地质资料 2
第2章 工艺设计方案的确定及构筑物的选择 3
2.1 污水处理厂的选址 3
2.2 污水处理工艺流程的确定 3
2.2.1 工艺流程选择 3
2.2.2可行性方案的确定 4
2.2.3污泥处理工艺流程 5
2.2.4 工艺流程方案的确定 6
2.3 主要构筑物的选择 6
2.3.1 格栅 6
2.3.2 沉砂池 6
2.3.3 初沉池 7
2.3.4 曝气池 7
2.3.5 消毒接触池 7
2.3.6 计量堰 8
2.3.7 污泥浓缩池 8
2.3.8 贮泥池 8
2.3.9消化池 8
2.3.10 污泥脱水 8
第3章 污水处理系统工艺设计 9
3.1粗格栅的计算 9
3.1.1原始设计参数 9
3.1.2进水格栅设计 9
3.2曝气沉砂池的计算 13
3.2.1池体计算 13
3.2.2 沉砂室尺寸计算 14
3.2.3 排砂设备 16
3.2.4 曝气系统设计计算 16
3.3.5 放空管 18
3.3.6 撇油 18
3.3 辐流初沉池的计算 18
3.3.1池体计算 18
3.3.2进出水设计 21
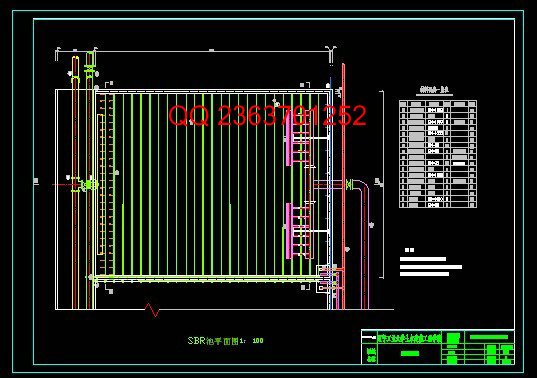
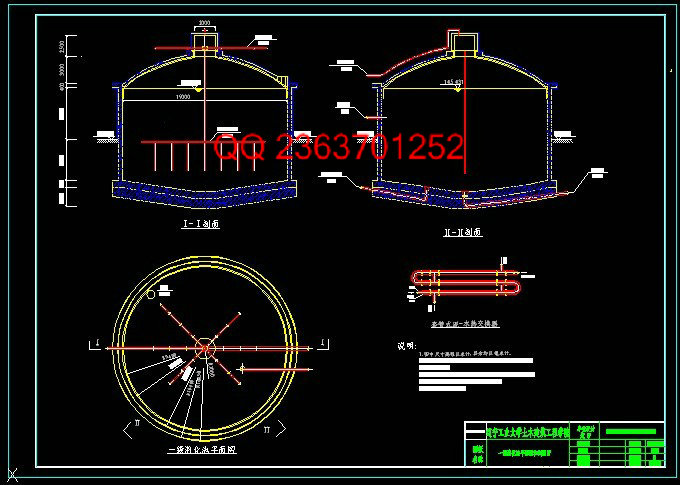
3.4 SBR池的计算 24
3.4.1 池体计算 24
3.4.2曝气系统设计与计算 27
3.4.3供气量 28
3.4.4 空气管道系统计算 29
3.4.5 空压机房 31
3.4.6 滗水器 31
3.4.7进出水管路设计 31
3.5 消毒接触池 32
3.5.1 接触池尺寸计算 32
3.5.2 加氯间 33
3.5.3排泥设施 33
3.5.4 混合装置 33
3.5.5 进出水设计 33
3.6 计量设备 34
第4章 污泥处理系统工艺设计 37
4.1 污泥浓缩池 37
4.2 贮泥池 38
4.3 污泥消化池 39
4.3.1 一级消化池构造尺寸 40
4.3.2 二级消化池构造尺寸 41
4.3.3 消化池各部分表面积计算 41
4.3.4 消化池热工计算 42
4.3.5 消化池保温结构的厚度计算 43
4.3.6 热交换器的计算 44
4.3.7 消化池污泥气循环搅拌计算 45
4.4 贮气柜 47
4.5脱水机房 47
4.6 事故干化场 48
第5章 污水处理厂总体布置 49
5.1 平面布置及总平面图 49
5.1.1 平面布置的一般原则 49
5.1.2 厂区平面布置形式 49
5.1.3污水厂平面布置的具体内容 50
5.1.4各构筑物单元的平面布置 50
5.1.5管渠和渠道的平面布置 50
5.1.6附属构筑物 50
5.2 污水处理厂高程布置 52
5.2.1污水处理构筑物的注意事项 52
5.2.2 污水水头损失计算 52
5.2.3 污泥水头损失计算 56
第6章 污水总泵站 60
6.1 概述 60
6.2 泵站设计 61
6.2.1 设计资料 61
6.2.2 泵房形式 61
6.3 泵站的设计计算 61
6.3.1 选泵 61
6.3.2 吸压水管路的设计 62
6.3.3 泵站水头损失计算 63
6.3.4 集水池 63
6.3.5 泵房的平面布置 65
6.3.6 泵站的高程布置 65
6.3.7 其他 67
第7章 土建及公共工程设计 69
7.1 土建工程和公共工程 69
7.1.1 土建工程 69
7.1.2 公共工程 69
第8章 污水厂投资估算与技术经济评价 71
8.1投资估算 71
8.1.1估算范围 71
8.1.2编制依据 71
8.1.3污水厂的直接费用 71
8.2劳动定员 73
8.2.1生产组织 73
8.2.2劳动定员 73
8.2.3人员培训 73
8.3运行费用和成本核算 74
8.3.1成本估算的有关单价 74
8.3.2运行成本估计 74
8.3.3运行成本的核算 75
第9章 结 论 77
参考文献 78
致 谢 79
|